| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- Operating System
- REACT
- JavaScript
- context switching
- Computer Science
- react 기초
- 비동기
- Python
- 자바스크립트
- 파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰
- python algorithm
- 파이썬
- 테스트코드
- 컴퓨터공학
- node.js
- 프로그래머스
- 알고리즘
- execution context
- 개발공부
- java
- 글또
- useState
- 자료구조
- codestates
- 운영체제
- 코드스테이츠
- algorithm
- 자바
- Zerobase
- OS
- Today
- Total
Back to the Basics
Java&SpringBoot-자바의유용한클래스들 본문
JAVA 5주차 수업 정리
자바의 유용한 클래스들
Achievement Goals
- JAVA의 유용한 클래스들에 대해서 알아본다.
- Object Class
- String Class
- StringBuilder Class
- StringBuffer Class
- text block Class
- Class Class
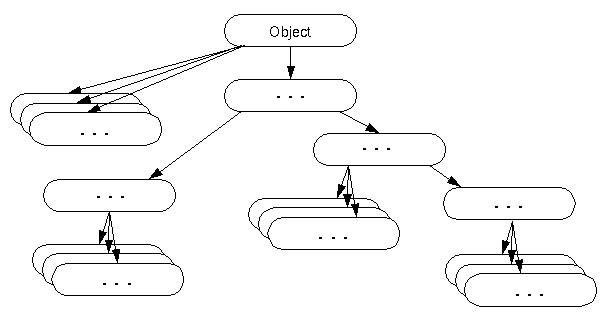
1. Object Class
1. Object Class란?
- 위의 문서에서도 설명하듯이 Object class는 java의 모든 class들의 최상위 class이다. 즉, 모든 Class는 Object Class를 상속받는다.
- 컴파일러에 의해 extendes Object가 추가된다.
- 부모 class의 참조 변수는 자식 class 객체를 참조할 수 있으므로, Object Class를 사용하면 어떤 타입인지 모르는 Object를 참조할 수 있다 (upcasting)
- Object Class의 메서드 중 일부는 Overriding 할 수 있다. 재정의 할 수 없는 method는 final로 선언되어있다.
- toString() method를 예로 들어보자.
- toString은 객체의 정보를 String으로 바꾸어서 사용할 때 쓰인다.
- String 또는 Integer의 경우 이미 Class에 toString리 overriding 되어있다.
- Overriding을 하지 않는 경우
class Book{ private String title; private String author; public Book(String title, String author) { this.title=title; this.author=author; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // test code Book book=new Book("programming","sora"); System.out.println(book); String str=new String("String Objec"); System.out.println(str); } /* 출력 ch01.Book@251a69d7 class의 full name --> 251a69d7 :JVM이 준 가상 메모리 16진수 String Objec 문장열이 나온다.이 경우 str.toString 이 자동으로 재정의 되어있기 때문이다. */
Book Object의 경우 JVM이 준 가상 메모리 주소가 출력이 되는데, String 객체는 이미 toString()이 재정의 되어있기 때문에 문자열로 출력이 된다.
- Overriding을 해보자. Book에 toString을 Overriding 하는 코드를 아래와 같이 추가하고 실행하면 String으로 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
class Book{ private String title; private String author; public Book(String title, String author) { this.title=title; this.author=author; } // 추가 코드 @Override public String toString() { return title + ',' + author; } } // test public static void main(String[] args) { Book book=new Book("programming","sora"); System.out.println(book); String str=new String("String Objec"); System.out.println(str); } /* 출력 programming,sora String Objec */
2. Object Class Methods
Object Class의 Method들을 공식문서 에서 퍼왔다. 아래와 같다.
이 중 많이 쓰이는 세 가지 메서드를 대한 예시 코드를 통해 알아보자.
1. equals() Method
- equals는 두 인스턴스의 주소 값을 비교하여 true false를 반환한다. 이 때 주소값을 heap memory의 주소값이다. (== 연산과 동일하다. 그리고 이 주소값을 hashCode라고 한다)
- 종종 인스턴스가 달라도 논리적으로 동일한 경우에는 true를 반환해야 하는 경우가 있다. 예를 들어 학번이 같은 instance는 같은 instance라고 할 수 있으므로 물리적으로는 다르지만 논리적으로는 같다.
- equals를 재정의하여 논리적으로 동일함 여부를 구현할 수 있다. 아래 코드로 확인해보자.
public class Student implements Cloneable{
private int studentNum;
private String studentName;
// Constructor
public Student(int studentNum ,String studentName) {
this.studentNum=studentNum;
this.studentName=studentName;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.studentName=name;
}
// equals Overriding
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Student) {
Student std=(Student)obj; // down casting
if(this.studentNum==std.studentNum)
return true;
else return false;
}
return false;
}
test code
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student std1=new Student(100,"sora");
Student std2=new Student(100,"sora");
Student std3=std1;
System.out.println(std1==std2); // false 다른 객체이므로
System.out.println(std1.equals(std2)); // 재정의 했으므로 true
System.out.println(std1==std3); // 주소가 같으므로 같음
}
/* 출력
false
true
true
*/std1와 std2는 물리적으로 다른 instance이다 (==비교) 하지만 재정의한 equals를 사용하여 논리적으로 같음을 구현할 수 있다.
2. hashCode() Method
- hash란 정보를 저장, 검색할 때 사용하는 자료구조로, 특정 키에 hash 함수를 적용하여 값을 반환한다
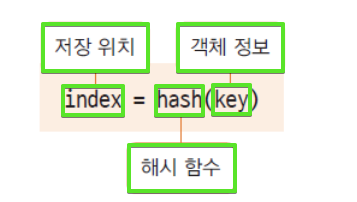
- JAVA에서 JVM은 hash방식으로 관리한다. hachCode는 Instance가 저장되어있는 heap 메모리의 주소 값을 반환하는 메서드이다.
- hashing 알고리즘에 의해 만들어지는 Integer 값을 return 한다.
- 두 개의 Instance가 같다는 것은 두 instance에 대한 equals()의 반환 값이 true로 동일한 hashCode() 값을 반환한다.
- equsl()를 재정의 하여 논리적으로 동일한 인스턴스의 경우에도 hashCode() 메서드도 재정의 하여 동일한 hashCode값이 반환되도록 해야 한다. 즉, 재정의를 할 때 equals()와 hachCode()는 pair이다.
- 위의 코드에서 hashCode를 Override 하고 결과를 확인해보자. 논리적으로 동일한 객체이므로 기준이 되는 한 개의 객체의 hash값만 return 하면 된다.
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return studentNum;
}
test code
Student std1=new Student(100,"sora");
Student std2=new Student(100,"sora");
Student std3=std1;
System.out.println(std1==std2); // false 다른 객체이므로
System.out.println(std1.equals(std2)); // 재정의 했으므로 true
System.out.println(std1==std3); // 주소가 같으므로 같음
System.out.println(std1.hashCode()); // 재정의 해서 같다.
System.out.println(std2.hashCode());
/* 출력
false
true
true
100
100
*/
- 이미 재정의가 되어있는 String과 Integer를 확인해보자
String str1=new String("abc");
String str2=new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // true
System.out.println(str1.hashCode()); // 96354
System.out.println(str2.hashCode()); // 96354
Integer i=100; // new X
System.out.println(i.hashCode()); // 정수값 100 이 나옴.
/* 출력
true
96354
96354
100
*/- 진짜 헤시를 찾아보자.
// 진짜 해시는? System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(std1)); System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(std2)); /* 출력 622488023 1933863327 */ - 재정의한 방법은 진자 해시가 아닐 수 있다. 진짜 헤시는 아래와 같은 방법으로 찾느다.
3. clone() Method
- clone() method는 객체의 원본을 복제하는 데 사용하는 메서드이다. 생성과정의 복잡한 과정을 반복하지 않고도 복제할 수 있다. (생성자를 생성하는 등..)
- clone() 메서드는 객체의 멤버 변수, 메서드 등의 객체의 정보가 동일한 또 다른 인스턴스가 생성되는 것이므로 객체지향 프로그래밍의 정보은닉, 캡슐화 등의 객체 보호 관점에서 위배될 수 있다.
- 그렇기 때문에 이 메서드의 사용을 허용해 준다는 의미로 cloneable interface를 명시해준다.(아래와 같이)
public class ClassName implements Cloneable{ ... ... } - 코드로 확인해보자.
// clone
std1.setName("kkkk"); // 생성이아니라 인스턴스의 상태를 그대로 복제.
Student copyStudent=(Student)std1.clone(); // clone의 리턴은 Object이므로 donwncasting
System.out.println(copyStudent);
/*출력
100:kkkk
*/2. String , StringBuilder, StringBuffer Class & text block
1. String Class
- Striing Class를 생성하는 방법으로는 heap memory에 Insctance로 생성되는 경우와 상수 풀(Constant pool)에 있는 주소를 참조하는 두 가지 방법이 있다.
- heap memory는 생성될 때마다 다른 주소를 갖지만, 상수 풀의 문자열은 모두 같은 주소를 갖는다.
- 한 번 생성된 String은 불변이다. 내부적으로는 char []에 들어가 있는데 final로 선언되어있다
public final classString - String을 + 연산으로 연결하면 기존의 String에 연결되는 것이 아닌 새로운 문자열이 생성된다. 아래의 코드로 환인 해보자
public static void main(String[] args) {
String java=new String("java");
String android=new String("android");
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(java));
// hash는 같게 나오므로 indentfyHashCode로
java=java.concat(android);
System.out.println(java);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(java));
// 메모리 주소가 바뀌는 것을알 수 있다.
}
/*출력
2060468723
javaandroid
622488023
*/
여기서 concat은 아래와 같이 String을 합친다.
concat(String str)
// Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.
concat을 하면 새로운 메모리에 저장이 된다. 하지만 이런 방법은 메모리 낭비가 될 수 있는 방법이다.
2. StringBuilder & StringBuffer
StringBuilder 공식문서 StringBuffer 공식문서
- 내부적으로 가변의 char를 멤버 변수로 갖는다.
- 문자열을 여러 번 연결하거나 변경할 때 사용하면 유용하다.
- String처럼 새로운 메모리를 생성하지 않고 char []를 변경한다.
- StringBuffer는 멀티 쓰레드 프로그래밍을 할 경우 동기화(Synchronization) 보장한다.
- 단일 쓰레드인 경우 StringBuilder 사용을 권장한다.
- 마지막에 toString() 메서드로 String으로 변환이 필요하다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String java=new String("java");
String android=new String("android");
StringBuilder buffer=new StringBuilder(java); // 매개변수로 str 가능
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(buffer)); // 동일
buffer.append(android);
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(buffer)); // 동일
String test=buffer.toString();
System.out.println(test);
}
/*출력
2060468723
2060468723
javaandroid
*/3. text block
java 13부터 사용이 가능하가 (아직 잘 쓰지 않는다)
html, json 문자열을 만드는데 유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String textBlocks="""
This is a example
of
textBlock
""";
System.out.println(textBlocks);
}
/* 출력
This is a example
of
textBlock
/*3. Class Class
공식문서에 따르면 Class class는 실행 중인 자바 애플리케이션의 Class와 Interface를 나타낸다고 한다.
생성자가 없으며 객체가 로드될 때 JVM에 의해 자동으로 생성되고 호출된다.
- JAVA의 모든 클래스와 Interface는 컴파일 후에 class파일이 생성된다. Class 클래스는 이 class파일을 로드하여 객체를 동적으로 로드하고 정보를 가져오는 메서드가 제공된다.
잘 이해가 되지 않으므로 메서드를 코드와 함께 보면서 이해해보자.
[Person Class]
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {}
public Person(String name,int age) {
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}만약 , p1이라는 obj가 어떤 타입인지 모를 때 Class object의 method를 사용할 수 있다.
// p1이라는 instance가 있을 때 type은 아래와 같이 알아낼 수 있다.
public static void getClassName(Object obj) {
System.out.println("The class of "+obj+" is "+obj.getClass().getName());
}
Person p1=new Person("sora",26);
getClassName(p1);
/*출력
The class of sora is ch04.Person
*/
이로써 p1은 Person이라는 클래스 타입이고 ch04 package에 있음을 알 수 있다.
- Class를 가져오는 방법은 아래와 같이 다양하다
- forName은 Class class의 method이다.
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
// - 클래스 이름으로 직접 Class 클래스 가져오기
Class c = String.class;
// - 생성된 인스턴스에서 Class 클래스 가져오기
String s = new String();
Class c = s.getClass(); //Object 메서드
동적 로딩 , 동적 바인딩
- 컴파일 시에 데이터 타입이 binding 되는 것이 아니고, running 중 데이터 타입을 동적으로 binding 하는 것을 동적 로딩, 동적 바인딩 이라고 한다.
- 프로그램을 만들 때에는 다른 타입의 변수로 처리를 했다가 runtime시에 원하는 class를 loading 하여 binding 할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
- Compile 시에는 타임이 정해지지 않기 때문에 동적 로딩 시에 오류가 발생하면 프로그램에 심각한 장애를 일으킬 수 있다.
Reflection programming
Package java.lang.reflrect 공식문서
- Reflection programming이란 객체를 통해서 Class의 정보를 분석해내는 프로그래밍 기법이다.
- 구체적인 Class의 정보를 알지 못해도 컴파일된 코드를 통해 역으로 정보를 알아낸다.
- 동적으로 객체를 생성하지 못하는 JAVA는 이 Reflection으로 그 역할을 대신한다.
- 만약, 로컬 메모리에 객체가 없는 경우에 사용한다 (원격 프로그래밍)
- 일반적으로 서로 다른 process인 경우 local이 아니다.
- java.lang.refllect package에 있는 class를 활용한다.
- 일반적으로 자료형을 알고 있는 경우에는 사용하지 않는다.
코드를 통해 알아보자
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 이런 경우는 reflaction programing이라고 한다.
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
Constructor[] cons=c.getConstructors();
for(Constructor co:cons) {
System.out.println(co); // String의생성자들을 볼 수 있다.
}
Method[] m = c.getMethods();
for(Method mth:m) {
System.out.println(mth); // String의 메서드들을 볼 수 있다.
}
}
/*
출력
public java.lang.String(java.lang.StringBuffer)
public java.lang.String(java.lang.StringBuilder)
public java.lang.String(byte[],int,int,java.nio.charset.Charset)
public java.lang.String(byte[],java.lang.String) throws java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException
public java.lang.String(byte[],java.nio.charset.Charset)
public java.lang.String(byte[],int,int)
public java.lang.String(byte[])
public java.lang.String(char[],int,int)
public java.lang.String(char[])
public java.lang.String(java.lang.String)
....
...
...
*/
'Programming Languages > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java&SpringBoot-Interface란? (0) | 2022.01.25 |
|---|---|
| Java&SpringBoot-Singleton-Design-pattern (0) | 2022.01.15 |
| Java & SpringBoot-Switch-Expression비교 (0) | 2022.01.11 |
| Java & SpringBoot-ObjectOriented-Class (0) | 2022.01.11 |
| Java & SpringBoot-StringObject (0) | 2022.01.11 |